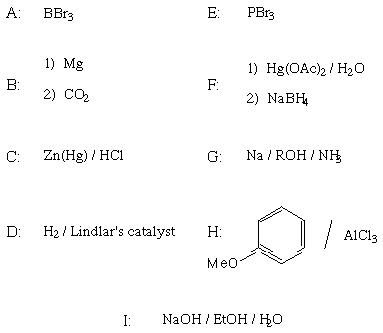
CHEMISTRY 3302 June 9, 1998
Instructions:
1) Neither calculators nor notes of any kind are allowed while
taking the exam. The periodic table is, of course, freely available.
Certain spectral tables are attached at the back of the exam.
2) Sign the first exam page at the top with your name (please
also print your name to ensure legibility). To be considered
for regrading, the exam must be taken in ink.
3) If a problem is giving you particular difficulty, go on with
other questions and return to it as time allows. The questions
are not necessarily in order of difficulty. Note that the
last problem is worth 42 points-make sure you get to it.
4) Concise explanations which expand upon your answers are encouraged. Partial credit will be liberally awarded if it is clear that you had the right idea, but simply made a small mistake at a later point in the answer. Don't get carried away, however, as this will waste your time.
Score
1 /30
2 /30
3 /20
4 /30
5 /20
6 /28
7 /42
Total
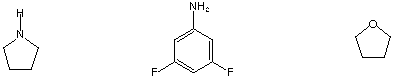
I. Molecular Properties (30 points)
Circle the one choice that fits the described property.
Best hydrogen bond acceptor

Shows strongest peak at M-15 in mass spectrum
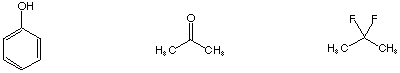
Is reduced by NaBH4
Antiaromatic
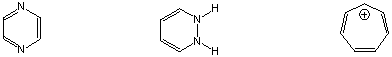
Longest wavelength UV absorption
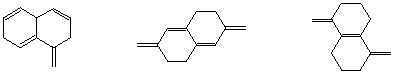
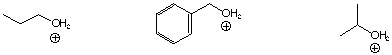
Most stable oxonium ion
II. Problems from Wade (30 points)
Do any two of these (if you work on all three,
indicate which two you want graded).
13-32. Show the mechanism for the following reaction:
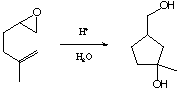
15-29f. What is the product of this reaction (show stereochemistry)?
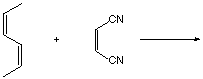
17-54. Triphenylmethanol (below) is insoluble in water, but when
it is treated with concentrated sulfuric acid, it dissolves to
create a bright yellow solution. On dilution of the solution with
more water, the color disappears, and triphenylmethanol precipitates
from solution. Explain this behavior (hint: construct an equilibrium
that generates something likely to be water soluble.
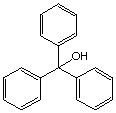
III. Mechanistic Organic Chemistry (20 points)
Show the mechanism for the following reaction:
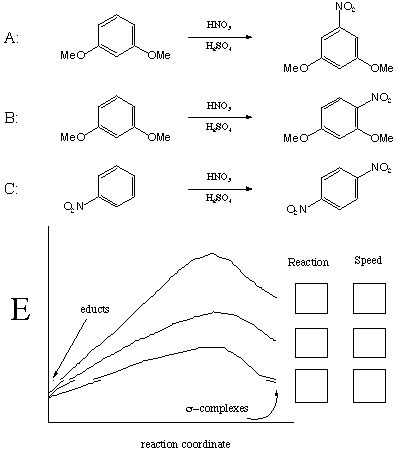
IV. Kinetics/Thermodynamics (30 points)
Label the three potential energy curves with their corresponding
reactions (A, B, or C) in the boxes under "Reaction".
In the boxes under "Speed", label the most rapid reaction
"fast", the slowest reaction "slow"
and the remaining reaction "average". Finally,
draw the s-complex for the fastest
reaction and explain why it is so stable.
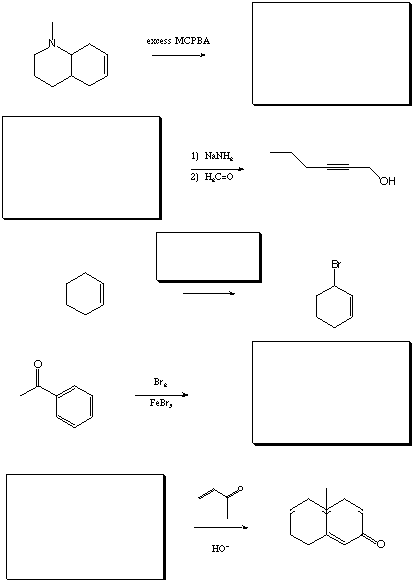
V. Synthetic Transformations 1 (20 points)
Fill in the boxes with the appropriate educts, reagents, or products.
A normal workup is assumed.
 VI. Synthetic Transformations
2 (28 points)
VI. Synthetic Transformations
2 (28 points)
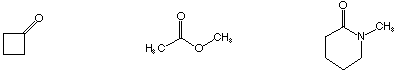
Show the sequence, with reagents, for accomplishing the two chain
lengthening/shortening (homologation/dehomologation) reactions
below.
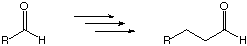
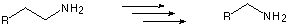
VII. Multistep Synthesis (42 points) (see next page
for instructions)
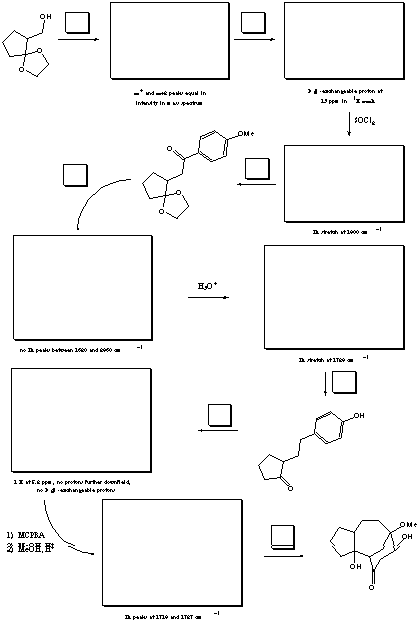
On this page is a list of 9 reagents (you may tear it off). You
will need 7 of these reagents to complete the total synthesis
outlined on the previous page (2 are not used). Fill in the
reagents by letter in the boxes over the reaction arrows.
The structures of the starting material, final product, and two
intermediates are provided, as are three sets of reagents. Draw
the correct structures for all other intermediates . Spectral
clues are listed under all of the structure boxes. A normal
workup is assumed for all reactions.
REAGENTS FOR PROBLEM VII: